Classification of Minerals(7. Phosphates, Arsenates and Vanadates)
7. Phosphates, Arsenates and Vanadates
Phosphates, arsenates and vanadates contain anionic complexes, PO43-, AsO43- and VO43- as fundamental units. Phosphates include monazite, vivianite, amblygonite, apatite, pyromorphite and turquoise. Erythrite and mimetite are members of arsenates. Vanadinite belongs to the vanadates.
Among these minerals, apatite is the most abundant, but the other minerals of this group are rarely found. Apatite is subdivided into fluorapatite, chlorapatite and hydroxylapatite according to the presence of anions, F-, Cl- and OH-. Monazite is a heavy mineral and may be concentrated in sands. Turquoise is characterized by its beautiful blue, bluish green or green colors and is used as a gemstone.
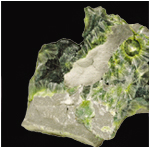
Wavellite USA
Wavellite, named after human name ‘Wavel’, is characterized by its radiating globular aggregates. On heating, it swells and splits into fine particles.

Carnotite USA
Carnotite is an important ore mineral of Vanadium and Uranium.

Vivianite Russia
Vivianite crystals show columnar, bladed or fibrous shape. It is easily soluble in water.

CuproadamiteGreece
Some zinc ions in adamite are replaced by copper ions to form cuproadamite.

Vanadinite Morocco
Vanadinite is an ore mineral of vanadium. It is characterized by low hardness, relatively high specific gravity and ruby-red, orange-red or brown colors.

ConichalciteUSA
Conichalcite is characteristically yellowish green to emerald green in color. Its Mohs hardness is about 4.5, and its specific gravity is about 4.3. It occurs as a secondary mineral in the oxidized zone of copper deposits.

Apatite Russia
Apatite occurs commonly as columnar crystals. It shows variable colors such as green, blue, violet, colorless, brown or even red with vitreous luster and white streak. Its Mohs hardness is about 5, and its specific gravity is 3.15 to 3.20. Apatite can be scratched by knife and soluble in acid.
Apatites are commonly found in all kinds of rocks (igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks) as well as in hydrothermal pegmatites and veins. According to the dominance of anions of either F-, Cl- and OH-, apatites are classified into fluorapatite, chlorapatite and hydroxylapatite, respectively. Phosphate rocks or fossil bones sometimes consist mainly of apatite in massive cryptocyrstalline form which is called collophane. Apatite has been used as a source material of fertilizer.